Visual field
Perimetry; Tangent screen exam; Automated perimetry exam; Goldmann visual field exam; Humphrey visual field exam
The visual field refers to the total area in which objects can be seen in the side (peripheral) vision as you focus your eyes on a central point.
This article describes the test that measures your visual field.
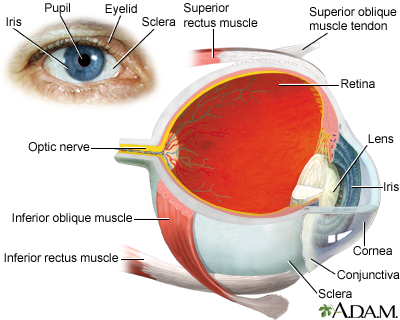
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer or tunic (sclera, or white, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (the retina) is nervous or sensory. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
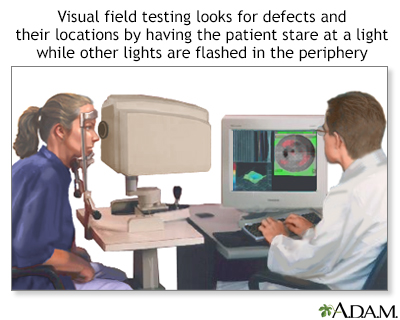
Central and peripheral vision is tested by using visual field tests. Changes may indicate eye diseases, such as glaucoma or retinitis.
How the Test is Performed
Confrontation visual field exam. This is a quick and basic check of the visual field. The health care provider sits directly in front of you. You will cover one eye, and stare straight ahead with the other. You will be asked to tell when you can see the examiner's hand.
Tangent screen or Goldmann field exam. You will sit about 3 feet (90 centimeters) away from a flat, black fabric screen with a target in the center. You will be asked to stare at the center target and let the examiner know when you can see an object that moves into your side vision. The object is usually a pin or bead on the end of a black stick that is moved by the examiner. This exam creates a map of your central 30 degrees of vision. This exam is usually used to detect brain or nerve (neurologic) problems.
Goldmann perimetry and Automated perimetry. For either test, you sit in front of a concave dome and stare at a target in the middle. You press a button when you see small flashes of light in your peripheral vision. With Goldmann testing, the flashes are controlled and mapped out by the examiner. With automated testing, a computer controls the flashes and mapping. Your responses help determine if you have a defect in your visual field. Both tests are often used to track conditions that may worsen over time.
Your provider will discuss with you the type of visual field testing to be done.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is necessary.
How the Test will Feel
There is no discomfort with visual field testing.
Why the Test is Performed
This eye exam will show whether you have a loss of vision anywhere in your visual field. The pattern of vision loss will help your provider diagnose the cause.
Normal Results
The peripheral vision is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to diseases or central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as tumors that damage or press on (compress) the parts of the brain that deal with vision.
Other diseases that may affect the visual field of the eye include:
- Diabetes
- Glaucoma (increased eye pressure)
- High blood pressure
- Age-related macular degeneration (eye disorder that slowly destroys sharp, central vision)
- Multiple sclerosis (disorder that affects the CNS)
- Optic nerve glioma (tumor of the optic nerve)
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- Pituitary gland disorders
- Retinal detachment (separation of the retina in the back of the eye from its supporting layers)
- Stroke
- Temporal arteritis (inflammation and damage to the arteries that supply blood to the scalp and other parts of the head)
Risks
The test has no risks.
References
Chuck RS, Dunn SP, Flaxel CJ; American Academy of Ophthalmology Preferred Practice Pattern Committee, et al. Comprehensive adult medical eye evaluation preferred practice pattern. Ophthalmology. 2021;128(1):1-29.
Idrees S, Sangave AA, Ramchandran RS. Visual fields in retinal disease. In: Sadda SR, Sarraf D, Freund KB, Hinton DR, Schachat AP, Wilkinson CP, eds. Ryan's Retina. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 13.
Olitsky SE, Marsh JD. Examination of the eye. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 637.
Schroeder R, Lind JT, Budenz DL. Visual fields. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 10.5.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 2/12/2023
Reviewed by: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
