Hyperthyroidism
Thyrotoxicosis; Overactive thyroid; Graves disease - hyperthyroidism; Thyroiditis - hyperthyroidism; Toxic goiter - hyperthyroidism; Thyroid nodules - hyperthyroidism; Thyroid hormone - hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
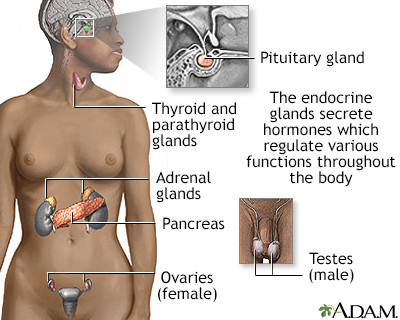
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
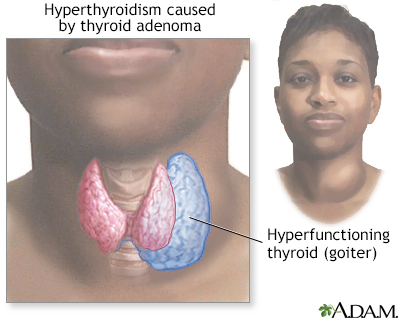
A goiter is a swelling in the neck due to an enlarged thyroid gland. The size may range from a single small nodule to a large neck lump. The swollen thyroid can put pressure on the windpipe and esophagus which can cause a cough, wheezing, breathing difficulties or swallowing difficulties. A goiter only needs to be treated if it is causing symptoms.
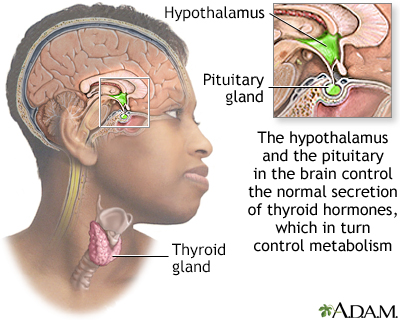
Although the thyroid gland releases the hormones which govern growth and metabolism, the brain (the pituitary and the hypothalamus) manages the release and the balance of the amount of hormones circulated.
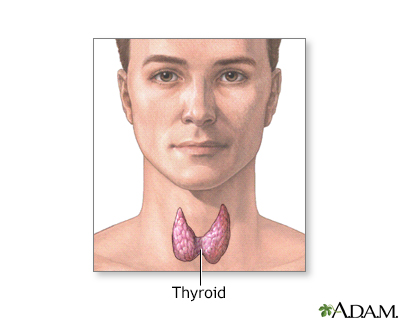
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Causes
The thyroid gland is an important organ of the endocrine system. It is located at the front of the neck just above where your collarbones meet. The gland makes the hormones that control the way every cell in the body uses energy. This process is called metabolism.
Many diseases and conditions can cause hyperthyroidism, including:
- Graves disease (most common cause of hyperthyroidism)
- Inflammation (thyroiditis) of the thyroid due to viral infections, some medicines, or after pregnancy (common)
- Taking too much thyroid hormone (common)
- Noncancerous growths of the thyroid gland or pituitary gland (rare)
- Some tumors of the testes or ovaries (rare)
- Getting medical imaging tests with contrast dye that has iodine (rare, and only if there is already a problem with the thyroid)
- Eating too much of foods that contain iodine (very rare, and only if there is already a problem with the thyroid)
You're restless and nervous. You feel hungry all the time, but no matter how much you eat, you keep losing weight. You can't sleep or concentrate, and you feel hot and sweaty. If symptoms like these are putting you on edge, the problem may be an overactive thyroid gland, or hyperthyroidism. This little butterfly-shaped structure in your neck is your thyroid gland. It's job is to release the hormones that help control your body's energy levels, a process known as metabolism. When you have hyperthyroidism, that little gland goes into overdrive, releasing too much of its hormones. Having too much thyroid hormone is like putting your body in fast forward, everything speeds up. That's why you feel shaky, hungry, and your heart feels like it's pounding. So, what causes hyperthyroidism? You can develop an overactive thyroid because you've gotten too much iodine, an element the thyroid uses to make its hormones. Or, you might have a growth on your thyroid that's causing the excess hormone production. But many people with hyperthyroidism have an autoimmune disorder called Graves disease, which also makes their eyes bulge out. During an exam, your doctor may notice that your thyroid is larger than normal, and that you have high blood pressure, tremors, or a fast heart rate. These can all be signs of hypothyroidism. You'll probably have a blood test to check the levels of your thyroid hormones. If you do have an overactive thyroid, you may need to take medicine to slow down the gland and its hormone production. Or, your doctor may suggest having surgery to remove some or all of the thyroid, or taking radioactive iodine to destroy it. If you have surgery or radioactive iodine treatment, you'll probably need to take thyroid hormones for the rest of your life to replace the ones your body can no longer make. You can't prevent hyperthyroidism, but once you have it, it's usually pretty easy to treat. With the right treatment you can finally be free from its symptoms. While you're being treated, watch out for an emergency condition called thyroid crisis, or thyroid storm, which can set in if you've been under a lot of stress or have an infection. If you have a fever, fast and unsteady heartbeat, or you feel less alert than usual, call your emergency services number or go to the ER right away.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Anxiety
- Difficulty concentrating
- Fatigue
- Frequent bowel movements
- Goiter (visibly enlarged thyroid gland) or thyroid nodules
- Hair loss
- Hand tremor
- Heat intolerance
- Increased appetite
- Increased sweating
- Irregular menstrual periods in women
- Nail changes (thickness or flaking)
- Nervousness
- Pounding or racing heart beat (palpitations)
- Restlessness
- Sleep problems
- Weight loss (or weight gain, in some cases)
Other symptoms that can occur with this condition:
- Breast development in men
- Clammy skin
- Diarrhea
- Feeling faint when you raise your hands
- High blood pressure
- Itchy or irritated eyes
- Itchy skin
- Nausea and vomiting
- Protruding eyes (exophthalmos)
- Skin blushing or flushing
- Skin rash on the shins
- Weakness of the hips and shoulders
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a physical exam. The exam may find the following:
- High systolic blood pressure (the first number in a blood pressure reading)
- Increased heart rate
- Enlarged thyroid gland
- Shaking of the hands
- Swelling or inflammation around the eyes
- Very strong reflexes
- Skin, hair, and nail changes
Blood tests are also ordered to measure your thyroid hormones TSH, T3, and T4.
You may also have blood tests to check:
- Cholesterol levels
- Glucose
- Specialized thyroid tests like Thyroid receptor antibody (TRAb) or Thyroid Stimulating Immunoglobulin (TSI)
Imaging tests of the thyroid may also be needed, including:
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of symptoms. Hyperthyroidism is usually treated with one or more of the following:
- Antithyroid medicines (propylthiouracil or methimazole) which reduce or block the effects of the extra thyroid hormone
- Radioactive iodine to destroy the thyroid gland and stop the excess production of hormones
- Surgery to remove the thyroid
If your thyroid is removed with surgery or destroyed with radioactive iodine, you must take thyroid hormone replacement pills for the rest of your life.
Medicines called beta-blockers may be prescribed to treat symptoms such as fast heart rate, tremor, sweating, and anxiety until the hyperthyroidism can be controlled.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Hyperthyroidism is treatable. Some causes may go away without treatment.
Hyperthyroidism caused by Graves disease usually gets worse over time. It has many complications, some of which are severe and affect quality of life.
Possible Complications
Thyroid crisis (also called thyroid storm) is a sudden worsening of hyperthyroidism symptoms that may occur with infection or stress. Fever, decreased alertness, and abdominal pain may occur. People need to be treated in the hospital.
Other complications of hyperthyroidism include:
- Heart problems such as fast heart rate, abnormal heart rhythm, and heart failure
- Osteoporosis
- Eye disease (double vision, ulcers of the cornea, vision loss)
Surgery-related complications, including:
- Scarring of the neck
- Hoarseness due to nerve damage to the voice box
- Low calcium level due to damage to the parathyroid glands (located near the thyroid gland)
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid)
Tobacco use may make some complications of hyperthyroidism worse.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Go to an emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have:
- Change in consciousness
- Dizziness
- Rapid, irregular heartbeat
Contact your provider if you are being treated for hyperthyroidism and you develop symptoms of underactive thyroid, including:
- Depression
- Mental and physical sluggishness
- Weight gain
References
Hollenberg A, Wiersinga WM. Hyperthyroid disorders. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 12.
Ross DS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, et al. 2016 American Thyroid Association guidelines for diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism and other causes of thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid. 2016;26(10):1343-1421. PMID: 27521067
Wang TS, Sosa JA. Management of hyperthyroidism. In: Cameron AM, Cameron JL, eds. Current Surgical Therapy. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:767-774.
Weiss RE, Refetoff S. Thyroid function testing. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ, de Kretser DM, et al, eds. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 78.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 8/12/2022
Reviewed by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
